
Hoisting & Lifting | Safety and Training | By Columbus McKinnon Training | 15 Jun 2020
Proper and routine hoist inspections are vital to ensuring safety and compliance during your lifting application. Pre-operational safety inspections help identify problems and address them before an incident may occur, reducing risk for personnel, your load, and your lifting system. This guide covers everything that operators should consider when performing a pre-operational hoist safety inspection.
This guide will walk you through the following topics for pre-operational hoist safety inspections:
- Safety Standards and Regulations
- The Difference Between Frequent and Periodic Hoist Inspections
- Markings and Labels
- Hoist Controls
- Hook Inspection (ASME B30.10)
- Operation Inspection
- Chain Inspection
Safety Standards and Regulations
When using hoisting equipment, it is very important to know and understand the safety and inspection standards that apply to your lifting system. Depending on the type of equipment you are using, different standards may apply. This can often be confusing as different regulations apply to different parts of the lifting system.
To explain, let’s start with an overview of the most important safety standards and which part of the lifting system they apply to.
ASME: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
ASME is an organization that provides design and inspection standards for hoists and rigging products. ASME is a voluntary committee made up of industry experts. Their standards are voluntary standards updated every three years – not laws like OSHA regulations. Standards are used as guidance for safety because many of our products do not have applicable OSHA regulations.
The first ASME standard you need to be aware of is ASME B30.16. This standard applies to underhung powered hoists, including electric and air, as well as chainfalls. This standard covers construction, marking, inspection, use, and training.
In the entertainment industry, these hoists are covered by ANSI E1.6-2. We recommend if you are in entertainment to obtain a copy of both standards.
ASME B30.16 Electric Hoists

ASME B30.16 Air Hoists / Pneumatic Hoists

ASME B30.16 Manual Hoists / Chainfalls

The second standard to be aware of is ASME B30.21, which applies to lever hoists, including chain, wire rope and strap hoists.
ASME B30.21 Lever, Wire Rope, Chain, and Strap Hoists

Where it gets complicated is that, in many cases, there are multiple safety standards you need to understand to use or inspect a single hoist. Take the CM Bandit for example:
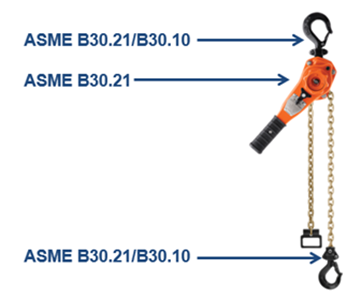
- ASME B30.21 applies to the entire hoist
- ASME B30.10 applies to hook inspection, how to use the hook properly, etc.
In this case, you have to understand two standards to ensure proper use and inspection of the Bandit hoist.
When using a full lifting system, the number of applicable safety standards can be even more overwhelming.
Below is a diagram of all the standards that can affect a single lifting system. Depending on whether you’re an operator or inspector, there are specific parts of these regulations you need to know in detail. When in doubt, always check with the equipment manufacturer.

It is highly recommended that anyone responsible for pre-operational hoist inspections be thoroughly trained by professional trainers. Find a comprehensive training program that includes frequent and periodical maintenance and inspection procedures.
The Difference Between Frequent and Periodic Hoist Inspections
There are two classes of hoist inspections: Frequent Inspections and Periodic Inspections.
Frequent Hoist Inspections
Frequent Hoist Inspections are what we refer to as Pre-Operational Inspections. These are the inspections we do between the Periodic Inspections. You do not need to maintain records of these inspections. We recommend that Frequent or Pre-Operational Inspections are conducted at the start of every shift to ensure the hoist is in safe working order. Frequent inspections allow you to determine if anything is wrong with the hoist before lifting a load.
Periodic Hoist Inspections
Periodic Inspections are thorough, detailed inspections that may require complete disassembly of the hoist. These inspections are conducted based on the hoist service (how often the hoist is used) as well as in which environment they are used. You must have a documented history of hoist inspection. Periodic inspections are required by OSHA, ASME and the manufacturers. Periodic inspections are written, documented inspections that you are required to keep on file to ensure your equipment is safe to use.
The type of service determines the inspection schedule:

If you find a lot of issues with a hoist during a Periodic Inspection:
- You may need to increase the number of inspections you conduct each year.
- Your operators may need to be trained to ensure they are using the hoist correctly. Hoists should not be damaged if they are being used properly.
While inspection records don’t need to be maintained for Frequent (Pre-Operational) Inspections, a pre-operational checklist can serve as a quick reference when conducting these inspections. The checklist provides a step-by-step guideline of essential items that should be checked during a Pre-Operational Inspection.
Although everything on this checklist may not pertain to every hoist, it is a good reminder of what to look for. The checklist does not NEED to be filled out before every shift. Even so, many companies require it to ensure operators are doing these checks and doing them correctly. We suggest that you laminate and zip tie the checklist to the hoist pendant, or somewhere on the hoist, to remind the operator to do it.
You can quickly and easily find authorized Columbus McKinnon service and repair centers here.
Markings and Labels

The first thing you want to check for during a Pre-Operational Inspection are markings. One type of marking to look for on the hoist is a lock-out tag or label. It is usually placed on a hoist during a repair or if the hoist has been taken out of service.
If you do find this type of marking on the hoist do not remove these tags or try to operate the hoist – there is a reason why the tag is there. It is also important to note that this tag must be removed by the person who put there.
Next, look for a tag or plate with hoist identification and capacity information. It should be stamped on or affixed to the unit.
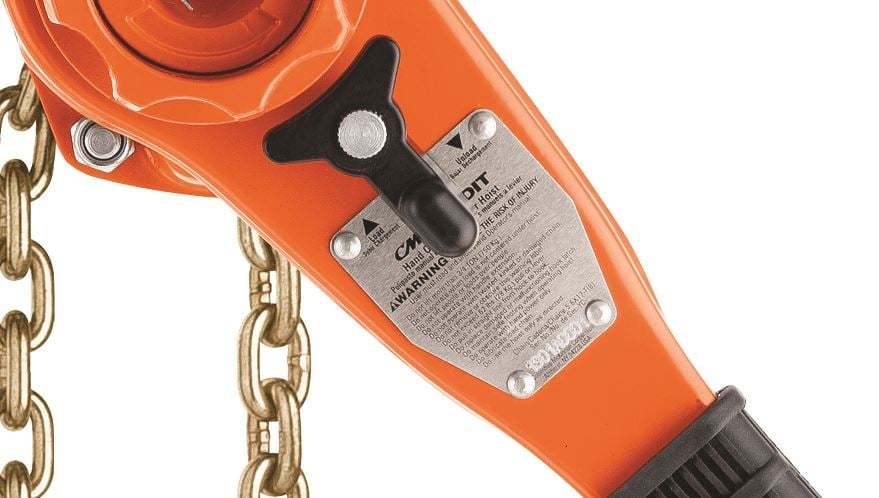

When you look at the CM Bandit nameplate, for example, the capacity should be clearly marked. The manufacturer, Columbus McKinnon, should also be identified and there should be a serial number. All hoists should have this information on them somewhere, whether it’s on a plate like you see on the Bandit or elsewhere.
Lastly, check the hoist for warning labels. Many hoists, like the Bandit, have this information on the same plate as the manufacturer and capacity. Some hand chain hoists have warning information on a plastic sleeve around the hand chain. Operators should not remove these. This warning information must be on the hoist somewhere for the hoist to be compliant with ASME B30.21 and ASME B30.16.
All operators should take the time to read and re-familiarize themselves with the warning information on the hoists they use. This will help refresh their memory and ensure they are using the hoist properly.
If this information is missing, especially if you cannot determine the capacity, you should not operate the hoist until you check with someone to get that information. This will help ensure safe operation and prevent injuries. Any hoist without these markings and labels should be taken out of service.
Hoist Controls
Before operating a hoist, it is critical to check the hoist controls. If a hoist control is not properly labeled or is not working correctly, people can get injured and loads and the surrounding environment can be damaged. There are two things to check when inspecting hoist controls. The first is the overall condition the control is in, including clear markings and labels. The second is whether or not the control functions properly. Let’s walk through each of these in detail.
Checking the Condition of your Hoist Control
Before operating a hoist, it’s important to check the condition of the pendant housing, buttons, and cables. Look for cracks, loose wires, and frays – anything that appears to be abnormal or unsafe. Specific areas to check include:
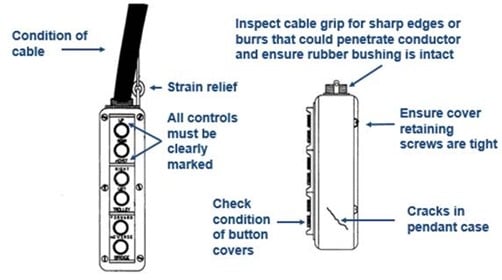
Below are some pictures of pendants we’ve collected. As you can see, pendants are typically abused. Here are some examples of what to look for:

In Figure 1, you can see a little orange wire sticking out on the right-hand side of the pendant. These pendants are live and therefore you could experience an electrical shock if you touch the wire. This exposed wire could also prevent the pendant from working properly or cause it not to work at all. This pendant should be fixed before use.
In Figure 2, you can see the pendant is very dirty, but this is not the issue you should be concerned about. Here we have a cracked button. When we push the button down, a metal plate makes contact with a live wire. If the button is broken, this is also a shock hazard. This button should be replaced before use.
In Figure 3, we have a zip tie holding the pendant together. Because there is a live power feed going to the pendant, this can cause an electrical shock. This pendant should be fixed and the zip tie removed before use.
If you see ANY of these issues or other unsafe conditions when you inspect your pendant, the hoist should be taken out of service until the pendant is repaired.
Checking Hoist Control Buttons: Markings & Operation
After you have ensured the pendant is in working order and safe to operate, you should test the buttons to make sure they are labeled clearly and correctly. You may be familiar with how to operate the controls, but if someone new had to use the hoist, could they identify what each button does? This test is one of the pre-operational tests you should always conduct before using a powered hoist.
A few warnings to keep in mind before you test the pendant’s operation:
- Ensure the area under the hoist or crane is clear of obstructions. Also, make sure there is no one under or in the path of the hoist, including yourself.
- Do not put a load on the hoist during this test.
- If the limit switch fails, make sure you do not run the bottom block into the hoist, drum or trolley. This action can damage the hoist. Please note that some hoists do not have limit switches.
- Be prepared to stop the hoist by releasing the controller.
Once you have taken these safety precautions, you are ready to operate and test the hoist controls. Just a quick check-in each direction is sufficient for this portion of the inspection. There is no need for extreme movements. To check for proper operation, follow the steps below:
- First, you need to verify the markings on the pendant are correct – that “up” moves the hoist up and “down” moves the hoist down.
- Test that the trolley controls move the trolley left or right as indicated on the pendant buttons.
- Test the bridge to ensure it moves as specified on the pendant.
- Check any warning devices on the pendant as well, if applicable. For example, horns, an indicator light, etc.
- Make sure controls were not modified or safety features were not disabled. One example is to disconnect a shut-off feature or extend or shorten operational switches. These features are intended to keep the operator safe. Do not operate any unit with modified controls.
- One suggestion: Marking the direction as “left” or “right” can be confusing depending on how the operator is standing, so we suggest labeling the controls with “north,” “south,” “east” and “west” to avoid any confusion.
- All functions of the hoist must work properly and as marked on the pendant. If not, the hoist must be taken out of service.
Once you have ensured the controls are clearly marked and functioning properly, you are ready to operate your hoist. Remember, if at any time in the future these issues are found with your control pendant, the hoist should be taken out of service until the controls are repaired.
ASME B30.10 Hook Inspection
ASME B30.10 covers hook inspection for all hoists, cranes and rigging hooks. Before operating a hoist, it is important to inspect the hook to ensure it is safe and free from defects before lifting a load. When inspecting the hook, there are a few key things to look for:
1. Deformation
Deformation can be an indication of overload, side loading or utilizing improper rigging techniques. In some cases, it may be apparent that the hook is deformed. Look for any bends, twists, cracks or sharp edges that could cut into your synthetic slings.
To check for less-apparent deformities, measure the hook’s throat opening. (Note: Typically this is not done during pre-operational inspections.) You should remove the hook from service if any distortion is noticeable. Check the throat opening. It should not be more than 5% or 1/4″ from the manufacturer’s original dimension. Check your manufacturer’s recommendations.
Also, some hooks have manufactured marks or bumps between the throat opening and the saddle of the hook. These are reference points for measurement. These can be found on our Hurricane 360° hoist. Each hoist manufacturer’s manual will tell you how to measure the hook.
2. Wear Corrosion
Look for excessive wear or corrosion on the hook. Any wear exceeding 10% of the original section dimension of the hook or its load pin means the hook should be removed from service.
3. Nicks & Gouges
There is an easy rule of thumb you can follow when checking for nicks and gouges – any nick or gouge that you can fit your fingernail into is cause to remove the hook from service.
serve as points to measure hook deformation, but, by making these marks, they have created stress areas that can cause the hook to easily fail.
As you can see in this example, these gouges were put here on purpose to
4. Latches
ASME states that hooks shall be equipped with latches and they have to be operable. Latches hold the rigging in the hook when in slack position. They are not meant to be a load-bearing piece, which can easily happen when using improper rigging techniques.
To check the latches, ensure that the latch bridges the throat of the hook when in the closed position and that it operates properly.
Hook latches are required unless it can create a hazardous condition. For example, if you have to climb on a load to release latch (fall hazard) instead of using a push stick to back the hook out of the attachment point.
5. Bolts & Pins

Check to make sure that all bolts and pins in the hook are secure. You can see in this example that the pin is sticking out which is a cause for concern. Check the pin to make sure the chain is properly connected to the hook block. Also check to make sure that the hook swivels and rotates freely when not under load.
6. Markings
Look for proper hook markings, including the manufacturer’s logo.
7. Field modifications

In this image, you see an example where someone welded on a sister hook. While this may be ideal for their application, these have heat damage and are ruined. If you need a unique hook, you should have an experienced manufacturer do this.
If any of these conditions are present or if you see anything on the hook that causes you concern, take the hook and/or hoist out of service until it can be replaced or repaired.
Operation Inspection
When testing the operation of the hoist, it’s important to test the upper and lower limits. A limiting device protects the hoist from getting damaged, from running the hook block into the hoist or running chain out of the hoist.
There are two types of hoists – hoists with a limit switch and hoists with a slip clutch.
If you have a hoist that uses a slip clutch in the up direction as its limiting device, like the CM ShopStar and the CM ValuStar, you should not do this test during your pre-operational inspection. This test would only be done during a periodic inspection.
If you have a hoist with a limit switch, you should conduct this test during your pre-operational inspection. If you are testing a two-speed hoist, you should test the limit switch at both speeds.
Before testing the limits of a powered hoist, there are a few safety precautions you should observe:
- Ensure the area under the hoist or crane is clear of obstructions. Also, check that there is no one under or in the path of the hoist, including yourself.
- Ensure there is not a load on the hoist.
- Be prepared to stop the hoist by releasing the controller.
After taking these precautions, follow these steps to test the hoist’s upper and lower limits:
- With no load on the hoist, start running up the hoist.
- Listen for strange noises.
- The limit switch should stop the hoist prior to the hook block hitting the hoist. If it fails to operate, or you think it will fail, do not run into the bottom of the hoist. This can damage the hoist.
- If the limit switch fails, the hoist needs to be removed from service.
- Next, lower the hoist hook to test the operation of the lower limit switch.
- Follow the same steps you took when testing the upper limit switch. As it is lowering, listen for unusual sounds.
- Check the chain or wire rope for defects.
- Again, if the limit switch fails, remove the hoist from service.
Testing your hoist’s upper and lower limits is an important part of your hoist pre-operational inspection. If at any time you have questions about the functioning of the limit switch on your hoist or think there is an issue, take the hoist out of service and contact the manufacturer.
Chain Inspection
The final step in our pre-operational hoist safety inspection should be to check the hoist’s chain.
Clean the chain, if required, before the inspection.
If the chain is dirty, it may be difficult to inspect. Therefore, it is important to make sure the chain is clean so you can see any damage. Inspect as much chain as you can. On hoists hung from overhead trolleys and beams, you will not be able to inspect the entire length of chain. Checking the entire length of chain will be part of a Periodic Inspection.
When conducting the hoist chain inspection, you should look for:
- Inner link wear, gouges, nicks, and twists: Inner link wear is difficult to see without moving links and is covered in detail during the Periodic Inspection. However, if something looks wrong, have someone check the chain in more detail.
- Bent or broken links
- Chemical damage or corrosion
- Stretch: Hoist chain does not stretch like lifting chain. It can be difficult to determine if the chain is stretched without measuring it. Full measurements are completed during the Periodic Inspection. However, if something looks wrong or out of proportion, take the time to measure the links. Chain sizes vary from hoist to hoist so you will need to refer to the product’s O&M manual to verify chain measurements.
Finally, check for proper lubrication.
Lubrication is important to extend the life of the chain and the hoist. It helps wear and helps the chain articulate properly. After you clean it for the inspection, make sure it is properly lubricated.
Here are some extreme examples of chain damage. Often wear will not be this apparent.
Important note to the stretched links image:
Hoist chain is not designed to stretch, whereas rigging chain is designed to stretch.

If you see anything of concern, take the hoist out of service and bring it to the attention of a trained hoist inspector for further evaluation.
Be Safe, Get Trained
Market demand for highly qualified technicians grow every year while OSHA, ASME, CMAA and HMI maintenance, repair and testing standards get more stringent. Thorough training and certification establish technical competence and credibility while ensuring consistent quality service standards and safe product use.
By staying up to date on regulations, training regularly, and following this guide, you're taking the necessary steps towards the safest application possible. Contact Columbus McKinnon's team of Professional Trainers for assistance with your application or custom training for your team.
Columbus McKinnon Training
Articles authored by "Columbus McKinnon Training" were written by industry professionals with decades of unique and in-depth experience in the material handling industry who are no longer employed by Columbus McKinnon.

Related Articles
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Hoist
A Guide to Specifying the Right Hoist for Your Application
Purchasing or specifying hoists to lift heavy objects in close proximity to equipment and/or personnel is a decision that deserves thoughtful consideration. In this article, we will identify some important items to factor into your decision-making process.



 Central America-Andean-Caribbean - EN
Central America-Andean-Caribbean - EN



